宝塔搭建wordpress网站,n127网推广,wordpress底部修改视频教程,石家庄学院原文链接#xff1a;https://blog.csdn.net/smstong/article/details/51145786
哈希表原理
这里不讲高深理论#xff0c;只说直观感受。哈希表的目的就是为了根据数据的部分内容#xff08;关键字#xff09;#xff0c;直接计算出存放完整数据的内存地址。
试想一下https://blog.csdn.net/smstong/article/details/51145786
哈希表原理
这里不讲高深理论只说直观感受。哈希表的目的就是为了根据数据的部分内容关键字直接计算出存放完整数据的内存地址。
试想一下如果从链表中根据关键字查找一个元素那么就需要遍历才能得到这个元素的内存地址如果链表长度很大查找就需要更多的时间.
void* list_find_by_key(list,key)
{for(plist;p!NULL; pp-next){if(p-key key){return p;}return p;}
}123456789
为了解决根据关键字快速找到元素的存放地址哈希表应运而生。它通过某种算法哈希函数直接根据关键字计算出元素的存放地址由于无需遍历所以效率很高。
void* hash_table_find_by_key(table, key)
{void* p hash(key);return p;
}12345
当然上面的伪代码忽略了一个重要的事实那就是不同的关键字可能产生出同样的hash值。
hash(张三) 23;
hash(李四) 30;
hash(王五) 23;123
这种情况称为“冲突”为了解决这个问题有两种方法一是链式扩展二是开放寻址。这里只讲第一种链式扩展。
也就是把具有相同hash值的元素放到一起形成一个链表。这样在插入和寻找数据的时候就需要进一步判断。
void* hash_table_find_by_key(table, key)
{void* list hash(key);return list_find_by_key(list, key);
}12345
需要注意的是只要hash函数合适这里的链表通常都长度不大所以查找效率依然很高。
下图是一个哈希表运行时内存布局
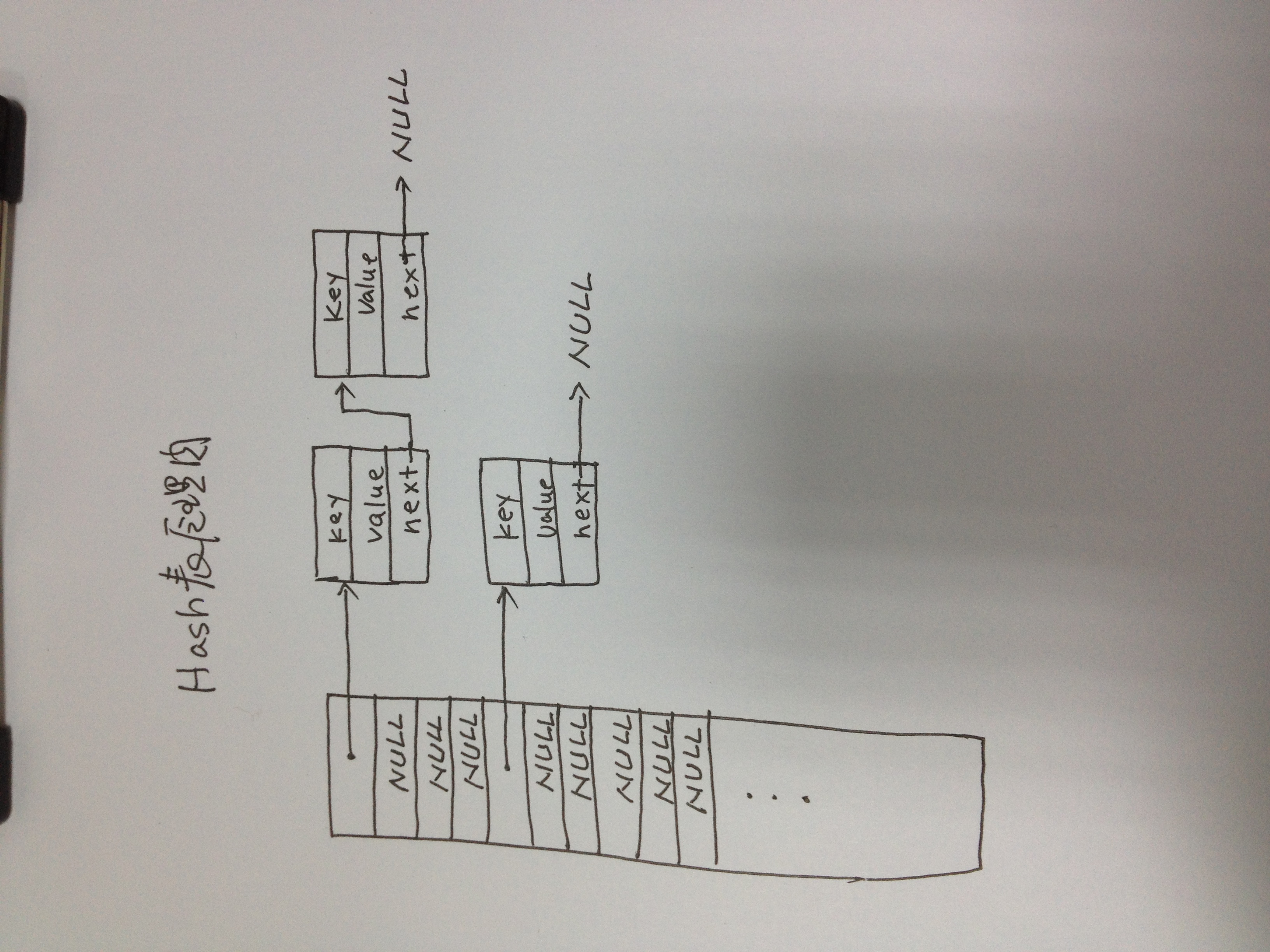
2 纯C实现源码
实际工作中大多数情况下关键字都是字符串的形式而大多数教科书上却使用整数关键字来举例这非常脱离实际。为此本人决定使用纯C语言开发一个哈希表结构供大家参考。主要特点
基于接口开发对外彻底隐藏实现细节具有自动释放客户结构内存的回调功能采用经典的Times33哈希算法采用纯C开发可供C和C客户使用
HashTable.h 头文件
#pragma once
typedef struct HashTable HashTable;#ifdef __cplusplus
extern C {
#endif/* new an instance of HashTable */HashTable* hash_table_new();/*delete an instance of HashTable,all values are removed auotmatically.*/void hash_table_delete(HashTable* ht);/*add or update a value to ht, free_value(if not NULL) is called automatically when the value is removed.return 0 if success, -1 if error occurred.*/#define hash_table_put(ht,key,value) hash_table_put2(ht,key,value,NULL);int hash_table_put2(HashTable* ht, char* key, void* value, void(*free_value)(void*));/* get a value indexed by key, return NULL if not found. */void* hash_table_get(HashTable* ht, char* key);/* remove a value indexed by key */void hash_table_rm(HashTable* ht, char* key);#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233
HashTable.c 实现文件
#include HashTable.h
#include stdlib.h
#include string.h
#include stdio.h#define TABLE_SIZE (1024*1024)/* element of the hash tables chain list */
struct kv
{struct kv* next;char* key;void* value;void(*free_value)(void*);
};/* HashTable */
struct HashTable
{struct kv ** table;
};/* constructor of struct kv */
static void init_kv(struct kv* kv)
{kv-next NULL;kv-key NULL;kv-value NULL;kv-free_value NULL;
}
/* destructor of struct kv */
static void free_kv(struct kv* kv)
{if (kv) {if (kv-free_value) {kv-free_value(kv-value);}free(kv-key);kv-key NULL;free(kv);}
}
/* the classic Times33 hash function */
static unsigned int hash_33(char* key)
{unsigned int hash 0;while (*key) {hash (hash 5) hash *key;}return hash;
}/* new a HashTable instance */
HashTable* hash_table_new()
{HashTable* ht malloc(sizeof(HashTable));if (NULL ht) {hash_table_delete(ht);return NULL;}ht-table malloc(sizeof(struct kv*) * TABLE_SIZE);if (NULL ht-table) {hash_table_delete(ht);return NULL;}memset(ht-table, 0, sizeof(struct kv*) * TABLE_SIZE);return ht;
}
/* delete a HashTable instance */
void hash_table_delete(HashTable* ht)
{if (ht) {if (ht-table) {int i 0;for (i 0; iTABLE_SIZE; i) {struct kv* p ht-table[i];struct kv* q NULL;while (p) {q p-next;free_kv(p);p q;}}free(ht-table);ht-table NULL;}free(ht);}
}/* insert or update a value indexed by key */
int hash_table_put2(HashTable* ht, char* key, void* value, void(*free_value)(void*))
{int i hash_33(key) % TABLE_SIZE;struct kv* p ht-table[i];struct kv* prep p;while (p) { /* if key is already stroed, update its value */if (strcmp(p-key, key) 0) {if (p-free_value) {p-free_value(p-value);}p-value value;p-free_value free_value;break;}prep p;p p-next;}if (p NULL) {/* if key has not been stored, then add it */char* kstr malloc(strlen(key) 1);if (kstr NULL) {return -1;}struct kv * kv malloc(sizeof(struct kv));if (NULL kv) {free(kstr);kstr NULL;return -1;}init_kv(kv);kv-next NULL;strcpy(kstr, key);kv-key kstr;kv-value value;kv-free_value free_value;if (prep NULL) {ht-table[i] kv;}else {prep-next kv;}}return 0;
}/* get a value indexed by key */
void* hash_table_get(HashTable* ht, char* key)
{int i hash_33(key) % TABLE_SIZE;struct kv* p ht-table[i];while (p) {if (strcmp(key, p-key) 0) {return p-value;}p p-next;}return NULL;
}/* remove a value indexed by key */
void hash_table_rm(HashTable* ht, char* key)
{int i hash_33(key) % TABLE_SIZE;struct kv* p ht-table[i];struct kv* prep p;while (p) {if (strcmp(key, p-key) 0) {free_kv(p);if (p prep) {ht-table[i] NULL;}else {prep-next p-next;}}prep p;p p-next;}
}123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263646566676869707172737475767778798081828384858687888990919293949596979899100101102103104105106107108109110111112113114115116117118119120121122123124125126127128129130131132133134135136137138139140141142143144145146147148149150151152153154155156157158159160161162163164165166167168169170171172173174
3 测试程序
下面是测试程序源码基于C。
测试程序test.cpp
#include stdio.h
#include stdlib.h#include HashTable.h// 要放入哈希表中的结构体
struct Student
{int age;float score;char name[32];char data[1024 * 1024* 10];
};// 结构体内存释放函数
static void free_student(void* stu)
{free(stu);
}// 显示学生信息的函数
static void show_student(struct Student* p)
{printf(姓名:%s, 年龄:%d, 学分:%.2f\n, p-name, p-age, p-score);
}int main()
{// 新建一个HashTable实例HashTable* ht hash_table_new();if (NULL ht) {return -1;}// 向哈希表中加入多个学生结构体for (int i 0; i 100; i) {struct Student * stu (struct Student*)malloc(sizeof(struct Student));stu-age 18 rand()%5;stu-score 50.0f rand() % 100;sprintf(stu-name, 同学%d, i);hash_table_put2(ht, stu-name, stu, free_student);}// 根据学生姓名查找学生结构for (int i 0; i 100; i) {char name[32];sprintf(name, 同学%d, i);struct Student * stu (struct Student*)hash_table_get(ht, name);show_student(stu);}// 销毁哈希表实例hash_table_delete(ht);return 0;
}12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728293031323334353637383940414243444546474849505152535455 link hrefhttps://csdnimg.cn/release/phoenix/mdeditor/markdown_views-e44c3c0e64.css relstylesheet/div